What is the future of 3D printing?
Additive manufacturing has already proven itself as a tool for prototyping and small-batch production. But the next frontier isn’t just about printing better parts — it’s about reshaping how entire industries design, source, and deliver products. So how will 3D printing change the world? By changing the systems that make it run.
The future of 3D printing lies in decentralization, digitization, and on-demand capability — and those shifts are already underway.
Manufacturing anywhere, anytime
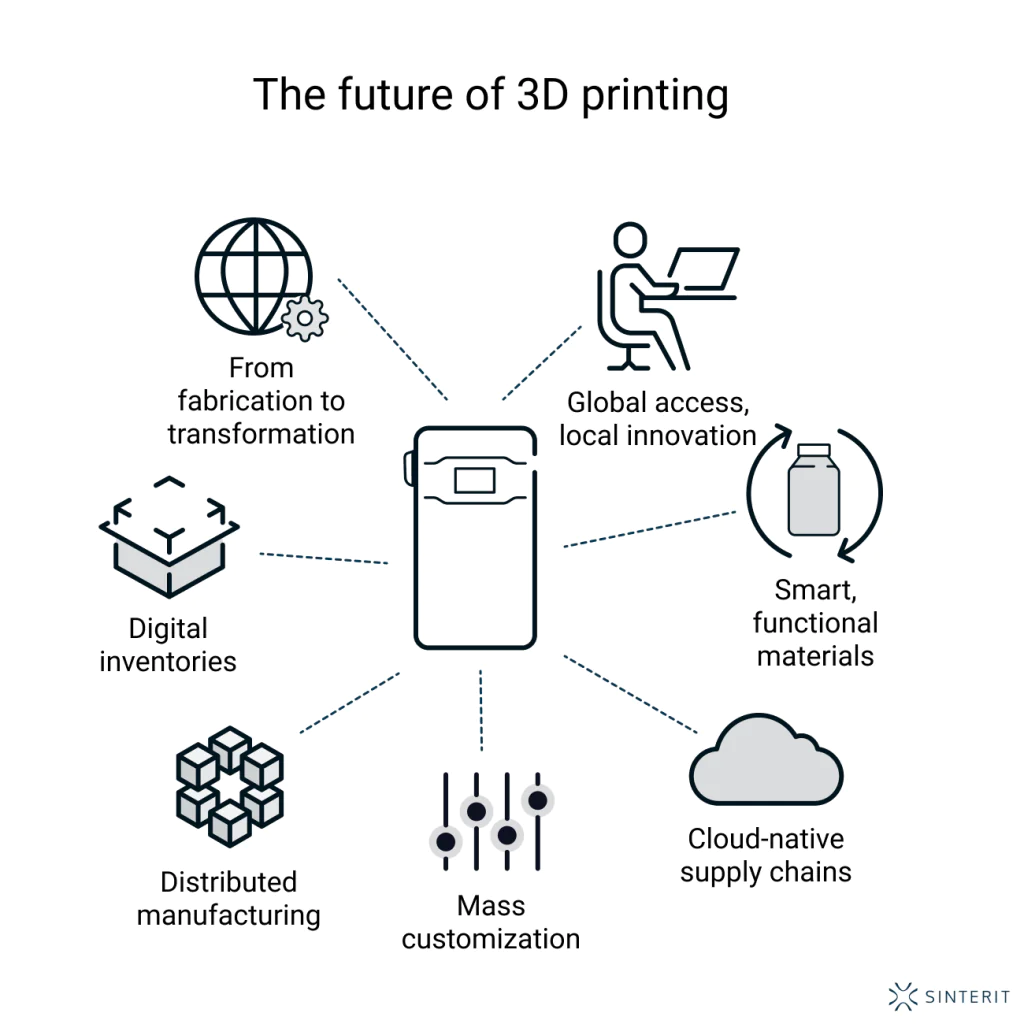
Perhaps the most transformative potential of 3D printing is its ability to bring production closer to the point of need. Instead of relying on centralized factories, goods can be manufactured locally, even remotely, using digital files and compact, versatile equipment.
This decentralization reduces reliance on global supply chains, shortens lead times, and allows for true just-in-time manufacturing. It also holds enormous potential in disaster zones, rural areas, or even space missions — where shipping spare parts is impractical or impossible.
Will 3D printing change the world? It already is — by redefining what “production” means and where it can happen.
From standardization to personalization
Mass production was built on the logic of identical parts. But consumers and industries are demanding more tailored solutions — whether it’s a custom medical implant, ergonomic tool, or uniquely styled consumer product.
3D printing enables mass customization at scale. Designs can be adjusted digitally with no tooling changes or added setup costs. This unlocks new business models based on personalization, short-run editions, or regionalized product variants — without sacrificing efficiency.
How is 3D printing changing the world? By shifting the design paradigm from “one-size-fits-all” to “fit-for-one”.
Smarter digital supply chains
In the near future, physical warehouses may give way to digital inventories — where spare parts, tools, and fixtures are stored as files rather than stock. These parts can be printed on-demand, close to where they’re needed, reducing overproduction and obsolescence.
This approach not only saves material but also strengthens resilience. Companies gain agility in responding to disruptions, market shifts, or design updates — with far less friction. Additive manufacturing becomes a key enabler of more responsive, digital-first logistics.
Material innovation and functional integration
While hardware will continue to evolve, the real leap lies in functional 3D printing — where parts are not just structures, but systems. Multi-material printers capable of embedding sensors, conductors, or actuators will allow us to create parts that sense, communicate, or respond to their environment right off the build plate.
We’re also seeing progress in bio-printing, conductive polymers, and smart composites that bring entirely new functionality into play. These advances blur the line between manufacturing and material science — and redefine what a “part” even is.
Education, democratization, and the next generation of makers
The accessibility of 3D printing is cultivating a new generation of engineers, designers, and problem-solvers. With affordable machines, open-source platforms, and cloud-based design tools, innovation is no longer confined to large R&D labs.
Students, startups, and hobbyists can now prototype and iterate on ideas with the same tools used in high-end industries. This democratization of manufacturing knowledge may be one of the most powerful long-term impacts of 3D printing — empowering local innovation on a global scale.
Looking ahead
So, what is the future of 3D printing? It’s not just more accurate printers or faster builds. It’s a fundamental shift in how we create, deliver, and experience the physical world. As the technology matures, its greatest influence may not be in how parts are made — but in how industries, economies, and people rethink what’s possible.
Explore also
- Is 3D printing the future?
- Future uses of 3D printing
- 3D printing vs traditional manufacturing
- What will 3D printers be used for in the future
- Trends in additive manufacturing
- AI in 3D printing
- Automation 3D printing
- Next-generation 3D printing materials
Related categories
 Austria
Austria  Bosnia and Herzegovina
Bosnia and Herzegovina  Bulgaria
Bulgaria  Croatia
Croatia  Czech Republic
Czech Republic  Denmark
Denmark  Estonia
Estonia  Finland
Finland  France
France  Germany
Germany  Greece
Greece  Hungary
Hungary  Ireland
Ireland  Italy
Italy  Latvia
Latvia  Lithuania
Lithuania  Poland
Poland  Portugal
Portugal  Romania
Romania  Slovakia
Slovakia  Slovenia
Slovenia  Spain
Spain  Sweden
Sweden  Switzerland
Switzerland  United Kingdom
United Kingdom  Ukraine
Ukraine  China
China  Hong Kong
Hong Kong  India
India  Israel
Israel  Japan
Japan  Malaysia
Malaysia  Philippines
Philippines  Saudi Arabia
Saudi Arabia  South Korea
South Korea  Taiwan
Taiwan  Thailand
Thailand  Turkey
Turkey  United Arab Emirates
United Arab Emirates  Egypt
Egypt  South Africa
South Africa  Tunisia
Tunisia  Canada
Canada  Mexico
Mexico  United States
United States  Brasil
Brasil  Colombia
Colombia  Australia
Australia  New Zealand
New Zealand