Investing in a Professional 3D Printer: The Ultimate Guide
Investing in a Professional 3D Printer can lead to the peak of transformation for your business and production, but it also carries significant risks. Is your company overlooking game-changing factors when starting this critical evaluation? This article outlines essential fundamentals to help engineers and purchasing teams determine the best direction when assessing a Professional 3D Printer.
Table of Contents
- The Abandoned Technology Peak: A Cautionary Tale
- The Mindset Before Assessing a Professional 3D Printer
- Why Your Project Might Require More Than Just a Professional 3D Printer
- Engineered for a Reason | Professional 3D Printers
- Choosing the Right Technology: What You Need to Know
- How to Make a Wiser Professional 3D Printer Assessment
- Investing Framework for an Optimal Professional 3D Printer
- Case Study: BNP and the Differentiator of SLS Technology
- The Final Verdict: How a Professional 3D Printer Becomes a Game-Changer
The Abandoned Technology Peak: A Cautionary Tale
Did you know that 80% of companies abandon 3D printing after purchasing the wrong technology? This results in low returns on investment, unforeseen expenses, and wasted potential. Many businesses invest heavily in high-end printers, only to discover they fall short in meeting production requirements or lack the scalability needed for growth. (Source: Additive Manufacturing Industry Report, 2020)
The Mindset Before Assessing a Professional 3D Printer
Disappointment is common among experienced business leaders who have invested in the wrong Professional 3D Printer or encountered underperforming technologies or vendors throughout their careers. This often leads to the confidence paradox—a loss of trust in considering state-of-the-art technologies, undermining future investments and hindering innovation in production
Why Your Project Might Require More Than Just a Professional 3D Printer
Many businesses begin with FDM (Fused Deposition Modeling) Professional 3D Printers due to their affordability and suitability for quick, low-volume prototypes or simple parts. For basic parts, FDM can be sufficient.
However, as prototyping and production scale up, the demand for higher-quality, detailed parts grows. At this point, FDM may struggle to meet the need for fine surface finishes and complex geometries. To satisfy these demands, businesses often continue using FDM for basic parts but turn to SLS (Selective Laser Sintering) when precision, surface finish, and the ability to handle intricate geometries are required. This is especially crucial in industries such as automotive, aerospace, and medical, where high-quality, durable parts are essential.
By integrating SLS Professional 3D Printers alongside FDM, businesses can optimize their production to meet both basic prototyping needs and high-quality, intricate end-use parts. Alternatively, businesses that require premium-quality products in very profitable sectors might choose SLS alone.
Engineered for a Reason | Professional 3D Printers
Here is a table illustrating how critical factors can influence your assessment when selecting a Professional 3D Printer. It compares two common technologies—FDM and SLS—though it’s important to note that many other 3D printing technologies may also be considered based on your specific needs.
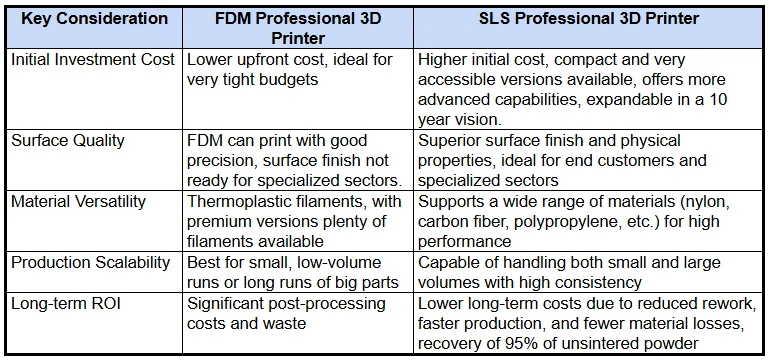
Choosing the Right Technology: What You Need to Know
A 10-Year Vision: The Holy Grail of Investment
The key to choosing the right Professional 3D Printer is aligning it with your primary production goals and ensuring it can be expanded in stages over the next 10 years. Recent data shows that 51% of manufacturers now use 3D printing for production parts, up from 35% last year. Additionally, 60% reported reduced prototyping costs, and 52% saw improved design flexibility (Protolabs Report).
How to Make a Wiser Professional 3D Printer Assessment
To make an informed decision, take a methodical approach to assess your needs using a structured framework. (below) Focus on the critical factors that matter most to your business, such as cost-effectiveness, customization, and long-term value. By understanding these core elements, you’ll be better equipped to choose the solution that aligns with your goals.
Investing Framework for an Optimal Professional 3D Printer
- Define Core Objectives | 10 Year Vision
Clearly outline your primary production goal:- Prototyping: Test models, refine designs
- Small/Medium Production: Custom part manufacturing
- End-use Parts: Functional components for customers
- High-Precision Models: Specialized, high-detail models
Key Question: What is your end goal, and how does it align with scalability?
- Technical Specifications & Materials
Identify critical characteristics and materials:- Strength: Will parts be stressed or require durability?
- Flexibility: Need for bending or elasticity?
- Precision: Tight tolerances and fine details
- Materials: PA12, PA11, metals, or high-temperature materials?
Key Question: What qualities and materials are essential for your application?
- Proof of Concept & Validation
Validate your choice with:- Simulations: Test digital performance
- Test Prints: Evaluate quality and accuracy
- Data Analysis: Ensure mechanical and thermal properties
Key Question: What tests are necessary to confirm your design?
- Total Cost of Ownership (TCO)
Consider the full cost:- Upfront Investment: Printer and accessories
- Operational Costs: Materials, maintenance, and labor
- Scalability: Can it grow with your production?
Key Question: Does the cost align with expected ROI and long-term savings?
- Industry-Specific Demands
Tailor your decision to industry needs:- Automotive, Aerospace, Medical: Precision, durability, compliance
- Consumer Goods: Flexibility and fast production
- R&D, Research & Education: Material experimentation and scalability
Key Question: How critical are industry standards?
Case Study: BNP and the Differentiator of SLS Technology
This Italian company specializing in ergonomic solutions for industrial production adopted Sinterit’s Lisa X 3D printer to improve the strength and surface quality of their components. Transitioning from FDM to SLS technology allowed BNP to produce functional parts with enhanced durability and aesthetics. Explore the BNP and Sinterit Case Study
The Final Verdict: How a Professional 3D Printer Becomes a Game-Changer
What is the most critical factor when investing in a Professional 3D Printer?
A clear 10-year vision is key; it helps ensure the printer is flexible enough and ready for scalability for prototyping, small-batch, or future production needs.
What costs are crucial when evaluating a professional 3D printer investment?
Consider the total cost: machine, maintenance, materials, and future scalability. In particular cases, the printer may give a cheaper appearance but be very expensive in the long term (materials, updates, licenses, open parameters).
Which 3D printer best suits your industry?
Opt for SLS printers for precision-focused industries like aerospace and medical. This ensures the printer will be more flexible for operation in diverse other sectors and ready for the more profitable ones.
How can you confirm the Professional 3D Printer’s performance?
Validate 2-3 printers with simulations or test prints before finalizing the price offerings. Ensure the Professional 3D Printer can handle complex parts and superior surface finishes.
 Author: Adrian Moreno
Author: Adrian Moreno
Senior Consultant: Leads global adoption of SLS technology, helping engineers and businesses define how to achieve advanced physical properties for specialized sectors from the very first step.













